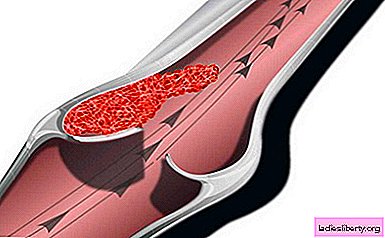
Thrombophlebitis is a disease that occurs as a result of an inflammatory process inside a vein, in the lumen of which a thrombus formation appears, narrowing the blood channel and impairing blood flow. Thrombophlebitis is a serious problem for people who, by occupation, are forced to spend most of their working time on their feet. Once developed varicose veins can be the main reason for further deterioration of the venous system, most often leading to thrombophlebitis.
Thrombophlebitis is superficial (affecting the upper layers of the veins) and deep (affecting the veins located inside the soft tissues).
Thrombophlebitis - Causes
As with most diseases of the musculoskeletal system, at risk of thrombophlebitis are primarily people who expose their bodies to frequent physical overload. Constant weight lifting is accompanied by a high degree of load on the legs and hips. It is in these departments that the deformation of veins most often begins. But you should not think that thrombophlebitis affects only active people. There are a number of reasons that provoke the onset of the disease.
Among them:
• Slow blood flow,
• Change in blood composition,
• Violation of normal blood coagulability,
• Vascular disease or injury,
• Disorders of a neurotrophic or endocrine nature,
• Infectious diseases,
• Allergic processes,
• Intravenous administration of drugs, accompanied by damage to the wall of the blood channel.
• Surgery, especially in the area of the hip joints and lower abdomen.
The disease is most often affected by people who have disorders in the activity of the cardiovascular system, or with various infectious manifestations and purulent inflammatory processes.
Thrombophlebitis - Symptoms
The manifestation of the disease depends on the size of the thrombus and the extent of the inflamed venous wall.
• Symptoms of thrombophlebitis of the lower leg. The first attack usually occurs suddenly and is accompanied by a feeling of fullness in the muscles of the calves of the legs and pain. When lowering the lower leg, the uncomfortable sensations sharply increase. The disease may be accompanied by fever. Edema is clearly visible in the inflamed area, and the skin becomes a light bluish tint. Touching, and especially squeezing, is painful for the patient.
• Symptoms of thrombophlebitis of the femoral vein. The pain syndrome is less pronounced due to the greater clearance and better blood flow than in the ankle of the legs. Obvious signs of femoral thrombophlebitis are pain in the limb and some bulging veins in the thigh, groin and pubic part. Body temperature can rise to a state of chills. Minor swelling of nearby muscles is possible.
• Symptoms of thrombophlebitis of the iliac-femoral region of the main vein. The most serious form of the disease that is tolerated by patients is quite difficult. If the blood clot did not completely block the lumen of the canal, then patients may not feel too sharp pains. But a certain discomfort occurs in the lower back and sacrum, as well as in the lower abdominal cavity in the vein lesion area. Sharp pains and deterioration of well-being begin with a complete overlap of the lumen of the vein. There is an increase in temperature to 39 degrees, malaise with signs of intoxication is noted. The place of appearance of the thrombus may have a completely white or cyanotic color, swelling occurs around.
Thrombophlebitis - diagnosis
Thrombophlebitis is diagnosed by palpation and determining the site that is causing the pain. To create a clearer clinical picture, rheovasography or ultrasound dopplerography is performed. The most informative is the ultrasound study using color-coded blood flow. Such a diagnosis not only determines the size of the thrombus, but also evaluates the quality of the affected vein and the degree of narrowing of its lumen.
Thrombophlebitis - treatment
Treatment and rehabilitation of patients with thrombophlebitis takes place in a hospital and under the strict supervision of specialists. First, until a final diagnosis is established, the affected limb is fixed in the patient, raising it above the surface by 15-20 degrees. Then, drug treatment is carried out, the essence of which is the administration of drugs that can break blood clots and prevent their further formation. After localization of inflammation, patients are shown spa treatment with baths containing hydrogen sulfide. In the most acute cases, a surgical method of treatment with venous ligation is used.
Even after undergoing inpatient treatment, patients should constantly wear elastic dressings that fix the problem areas of the veins.











